Top Tax Saving Options Other than Section 80C

Buy Life Insurance in under 5 minutes and Save upto 75%*
All About Tax Saving Investments Other than 80C
Section 80 C is an extremely popular provision of the Income Tax Act of the year 1961, under the discount up to ₹1.5 Lakh is provided on a number of loan products and other tools of investment.
However, you must also be well-informed about several different instruments with the aim to reduce the part of your taxable income. Such options of saving tax other than 80C offers you the ability to increase your savings annually through substantial returns of income tax.
As the Income Tax Act holds several provisions for tax returns, an individual may not be well aware of all the regulations simultaneously. This may cause them to lose on several funds through redundant payment of taxes, bringing down the annual savings along the way respectively.
We look forward to helping you in keeping a track of total taxable income by elaborating the different provisions which help in saving tax other than 80C in total.
Except the 80C, what are the various tax-saving investments?
Except 80C, income tax saving instruments can be mentioned under the following acts:
1. Interest Income on Savings Account Deposits
Section-80TTA
Limit – ₹10,000
Section 80TTA allows you to deduct the total amount of interest earned on savings account deposits. However, the deduction of this kind from taxable income is restricted to ₹10,000 each year.
If you have many savings accounts with various institutions, the entire accumulated interest is considered and taxed as “income from other sources.”
If this interest income surpasses ₹10,000 in a calendar year, only the extra amount is subject to tax at rates based on aggregate yearly income.
2. Interest Paid on Education Loan
Section - 80E
Limit – No limit
Under this clause, income used to pay the interest component of student loans cannot be taxable. According to the sum of funds necessary, an education loan of this kind can either be unsecured or secured.
It ought to be emphasized, however, that these kinds of waivers are given only for the first eight years of repayment of loans. Any income used to cover the burden of interest outside this period is taxed.
Education loans qualifying for these deductions must be taken out in the full name of the person in question and may be utilized to cover the higher education costs of the person in question, their spouse or children. Other than 80C, it constitutes one of the most prominent tax-saving methods.
3. Premium Payment for Health Insurance Policies
Section – 80D
Limit- Depends on conditions
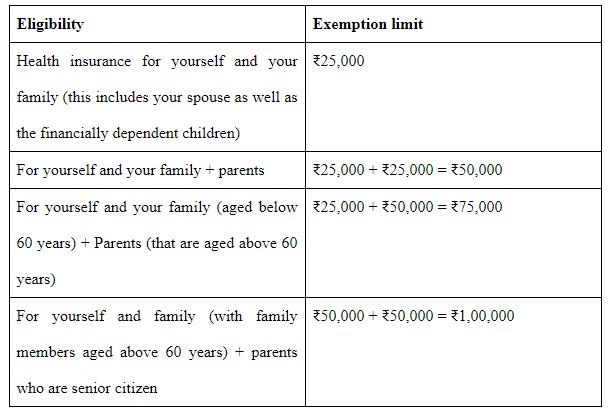
Section 80D tax breaks are now available for medical examination charges as well. You are eligible for a tax exemption for such expenses up to ₹5,000.
This exemption includes a rebate of ₹25,000 on health insurance. This implies that customers who made a claim of ₹5,000 for health check-up costs are eligible for a ₹20,000 premium charge rebate.
4. Interest Component Waged For Home Loans
Section - 24(b)
Limit – ₹2 Lakh
Under this clause, interest payments of a home mortgage are exempt from income tax computations. If the residence is purchased for personal use, a maximum of ₹2 Lakh may be obtained as a tax deduction on the interest rate, as long as the building has been finished within the first five years of the loan’s term.
If you opt to lease out the bought property, no tax is due on the interest portion of the home loan.
5. Interest Component Spent For Home Loans for First-Time Home Buyers
Section – 80EEA
Limit – ₹50,000 over Section 24 advantages (b)
New homeowners can get an extra interest benefit of fifty thousand rupees above Section 24(b) on their mortgage EMIs of the home’s value is less than ₹45 lakh. Other than Section 80C, this effectively allows for a tax savings of up to ₹2.5 lakh.
However, no previous property must be registered in the property owner’s name while applying for a house loan in order to be qualified for a tax deduction on the total amount spent on the payment of interest under Section 80EEA.
6. Maturity Sum Assured on Life Insurance Plans
Section -10 (10D)
Limit – Entire maturity amount
Section 10 allows for a tax credit on the total sum guaranteed paid upon completion of life insurance or the premature death of an insured individual (10D).
However, if the death benefit is received after April 1st, 2012 and the total value premium costs are lower than the entire amount promised, it is exempted from tax computations.
If the insurance is purchased before April 1st, 2012 the cost of premium must be under 20 percent of the total sum insured in order to qualify for waivers under section 10 (10D).
7. House Rent Allowance Included in Salary Break-Up
Section -10 (13A)
Limit – Predetermined conditions
This section of the Income Tax Act applies to tax advantages under house rent allowances (HRA), assuming your salary breakdown includes the HRA component. The overall exemption provided under this program is equal to the sum of the following:
- Actual annual HRA payments made.
- 50% of annual pay for individuals living in cities
- 40% of annual salary for persons residing in non-metropolitan areas
- Annual rent paid less 10% of basic income + DA
8. House Rent Allowance Component Excluded From Salary Break-Up
Section – 80G (G)
Limit – Predetermined conditions
If your employer does not include the HRA component in your pay breakdown, you may claim Section 80G (G) exemptions on all of your taxable income. Other than 80C, these tax-saving investments provide waivers up to the lowest value of the given parameters:
- 5,000 rupees every month.
- 25% of one’s overall annual earnings.
- Annual rent less 10% of gross annual income.
9. Donations Provided to Charitable Organisations
Section - 80G
Limit – No limit
Section 80G exempts all income donated to charity organizations from the calculation of taxes. There is no cap on such tax breaks if the transfers are conducted through different banks.
Cash donations of up to ₹2,000 are exempted from taxation. Such payments, however, must be paid to recognized charitable organizations.
10. Donations Made to the Scientific Research and Rural Development
Section- 80GGA
Limit- No limit
Section 80GGA allows for tax exemptions on gifts made for Scientific Research and Rural Development.
Such reductions are available for totality of income spent, providing the transaction is performed through a given bank account which is already recorded.
11. Donations Made to Political Parties
Section – 80 GGC
Limit- No Limitation
Except for Section 80C, donations to political parties are tax deductible. If the contribution in question was made via wired bank transfer, the whole sum is exempted from tax computations.
In addition, under Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act (RPA) of 1951, the political party for which such contributions were given must be registered.
12. Expenses Incurred With Respect to Treatment of a Disabled Person
Section – 80DD
Limit:
- ₹75,000 for roughly 40%-80% disability
- ₹1,25,000 for higher than around 80% disability
Individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) who contribute to the medical care and happiness of a disabled member of their family are eligible for Section 80D (D) exemptions on the entire revenue used for covering up of such expenses.
The coverage limitation depends on the extent of disability, with people having almost 40-80% disability qualifying for a deduction of up to ₹75,000.
Families who house a person with a disability of more than 80% are eligible for up to ₹1.25 lakh of claim, which includes all related expenses. Such claims are exclusively available to the reliant individuals’ families.
13. Income Tax Benefits Extended For Disabled Individuals
Section - 80U
Limit:
- ₹75,000 for around 40%-80% disability
- ₹1,25,000 for higher than 80% disability
Individuals who are disabled can seek compensation in the way of tax exemptions under Section 80U. A registered medical professional must certify such disability with a minimum of 40% impairment.
Individuals with around 40-80% disability are eligible for ₹75,000 in tax benefits, while those with more than 80% disability can receive up to ₹1.25 Lakh in tax benefits.
14. Expenses Incurred For Treatment of Individuals Having Specific Disease or Disability
Section - 80DDB
Limit - ₹40,000 (₹1,00,000 for senior citizens)
People who pay for medical care of reliant family members who suffer from certain disorders are eligible for tax breaks on eventual income.
In such instances, the entire amount of ₹40,000 is distributed to those under the age of 60. As a result, the waiver is increased to one lakh rupees for elderly persons (60-80 years) and super elderly people (above the age of 80 years).
Such waivers are available to cover the care of serious illnesses like neurological diseases (producing 40% or greater disability), malignant malignancies, AIDS, chronic renal failure and haemophilia.
Thus, there are various tax-saving strategies besides Section 80C that can successfully raise your overall wealth with time. Most tools also function as comprehensive investing tools, allowing for larger returns or lowering mandatory expenses.